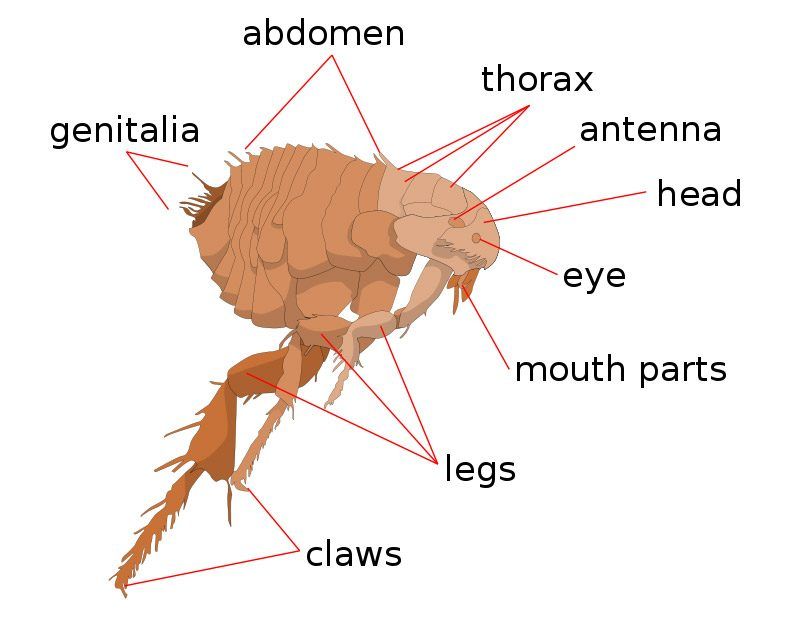
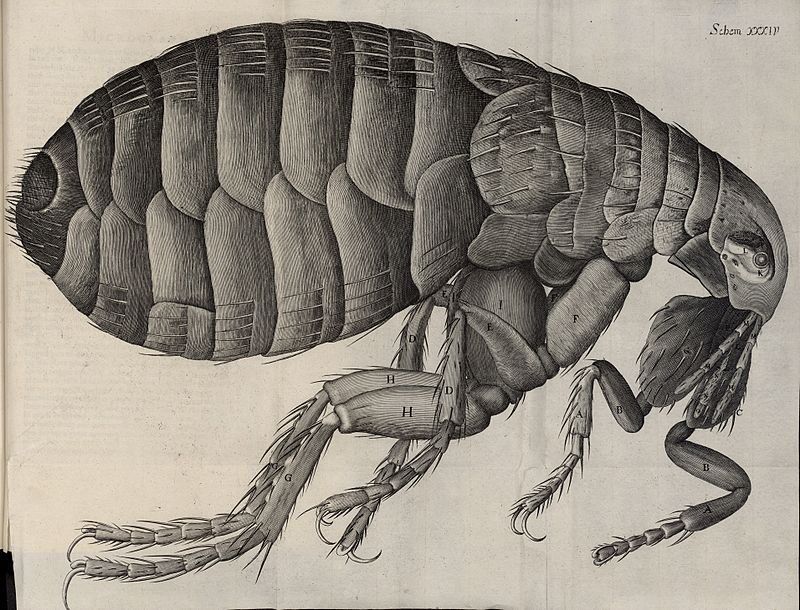
FLEAS
Fleas are small (1/16 to 1/8-inch (1.5 to 3.3 mm) long), agile, usually dark colored (for example, the reddish-brown of the cat flea), wingless insects with tube-like mouth-parts adapted to feeding on the blood of their hosts. Their legs are long, the hind pair well adapted for jumping: a flea can jump vertically up to 7 inches (18 cm) and horizontally up to 13 inches (33 cm).[3] This is around 200 times their own body length, making the flea one of the best jumpers of all known animals (relative to body size), second only to the froghopper. According to an article in Science News [4], “researchers with the University of Cambridge in England have shown that fleas take off from their tibiae and tarsi — the insect equivalent of feet — and not their trochanter, or knees. The researchers report their conclusion in the March 1 Journal of Experimental Biology.” It has been known that fleas do not use muscle power but energy stored in a protein named resilin but the researchers used high-speed video technology and mathematical models to discover where the spring action actually happens. Their bodies are laterally compressed (human anatomical terms), permitting easy movement through the hairs or feathers on the host’s body (or in the case of humans, under clothing). The flea body is hard, polished, and covered with many hairs and short spines directed backward,[5] which also assist its movements on the host. The tough body is able to withstand great pressure, likely an adaptation to survive attempts to eliminate them by mashing or scratching. Even hard squeezing between the fingers is normally insufficient to kill a flea. It is possible to eliminate them by pressing individual fleas with adhesive tape or softened beeswax (or “cheese” wax) or by rolling a flea briskly between the fingers to disable it then crushing it between the fingernails. Fleas also can be drowned in water and may not survive direct contact with anti-flea pesticides.
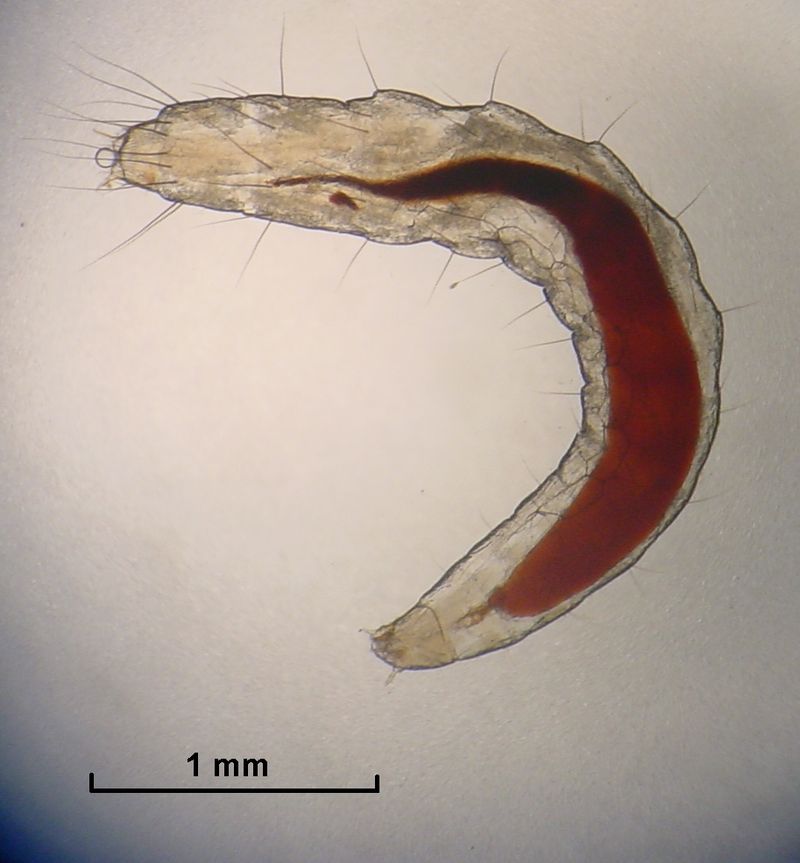
Fleas lay tiny white oval-shaped eggs better viewed through a loupe. The larva is small, pale, has bristles covering its worm-like body, lacks eyes, and has mouthparts adapted to chewing. The larvae feed on various organic matter, especially the feces of mature fleas. The adult flea’s diet consists solely of fresh blood.[6] In the pupal phase, the larva is enclosed in a silken, debris-covered cocoon.
Flea Life Cycle & Habitat
Fleas are holometabolous insects, going through the four life cycle stages of egg, larva, pupa, and imago (adult). The flea life cycle begins when the female lays after feeding. Adult fleas must feed on blood before they can become capable of reproduction.[5] Eggs are laid in batches of up to 20 or so, usually on the host itself, which means that the eggs can easily roll onto the ground. Because of this, areas where the host rests and sleeps become one of the primary habitats of eggs and developing fleas. The eggs take around two days to two weeks to hatch.[3]